By: DR.KRISTIAN ALEXANDER
As world leaders, delegates and visitors embarked on the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP 28) in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, the intersection of climate change and religion featured prominently. This gathering of global leaders provided an unparalleled platform for religious institutions to amplify their advocacy for urgent and meaningful action on climate change.
Religious traditions, often regarded as moral compasses, carry a unique capacity to inspire and mobilize communities towards environmental stewardship. COP 28 offered an opportunity for faith leaders to elevate their voices, emphasizing the moral imperatives embedded within their teachings and calling for a collective response to the climate crisis.
Historically, religious institutions were often perceived as silent on matters of environmental concern. However, the realities of climate change have sparked a re-examination of sacred texts and doctrines, prompting a renewed focus on humanity’s moral responsibility to protect the Earth.
Many religious traditions, including Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism, and indigenous spiritualities, share a fundamental principle: the Earth is not just a resource but a sacred trust. In Christianity, the notion of stewardship, the responsibility to care for God’s creation, resonates strongly. The Evangelical tradition has also witnessed a growing movement known as Creation Care, advocating for a proactive role in environmental conservation.
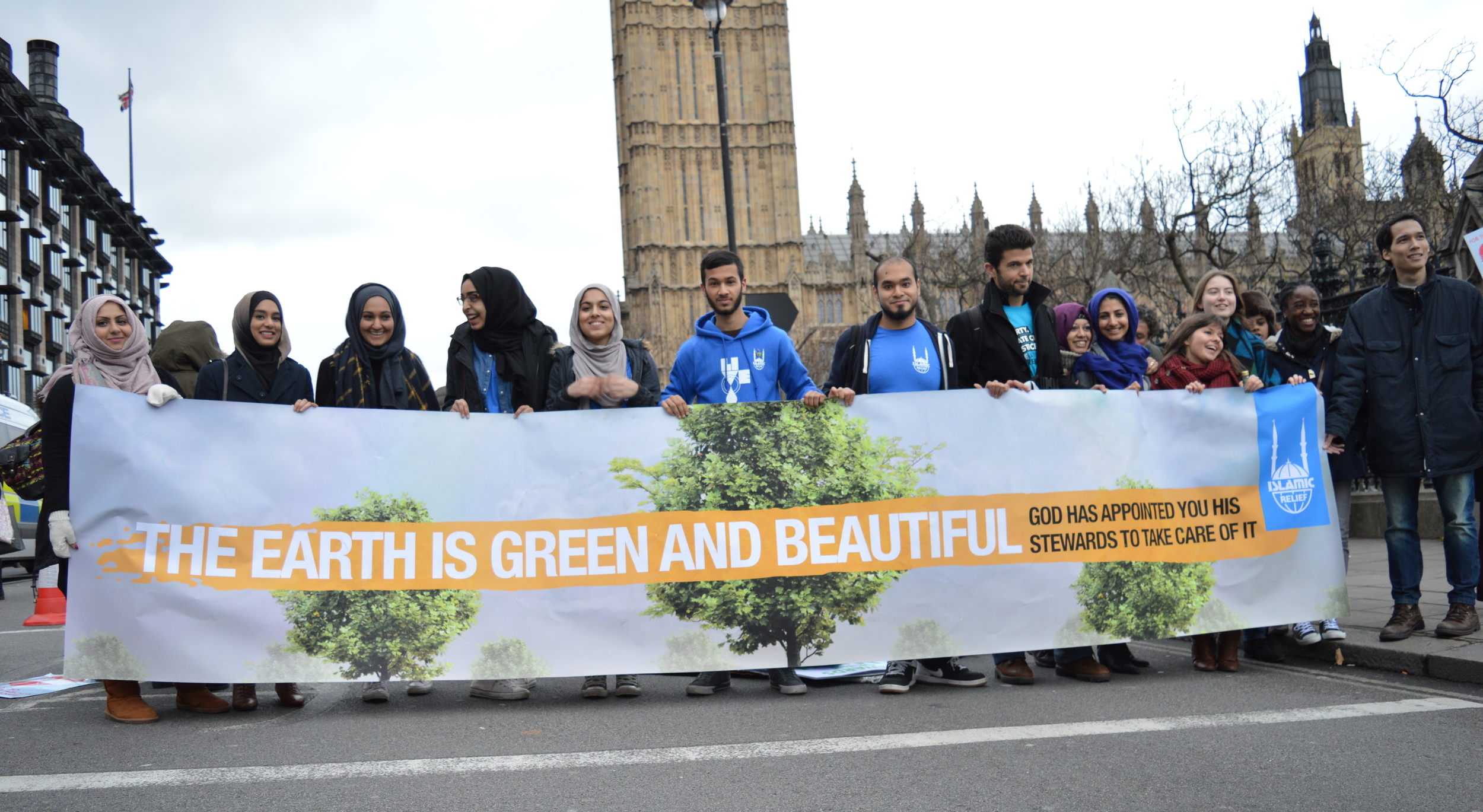
Within Islamic teachings, believers are considered stewards of the Earth, emphasizing ethical treatment and responsible use of resources. Buddhism, with its emphasis on interconnectedness, inspires a reverence for all living beings, fostering a sense of responsibility for the environment. Hinduism’s sacred landscapes and the principle of ahimsa, or non-violence, guide believers toward sustainable practices.
One significant player in this intersection is Pope Francis, who has consistently championed environmental consciousness within the Catholic Church. The upcoming conference presents an ideal forum for the Pope to renew his call for global cooperation and sustainable practices. The moral authority of religious figures can act as a bridge between diverse nations and communities, fostering a shared commitment to preserving our planet.
Pope Francis, in particular, has been a vocal proponent of environmental consciousness. His 2015 encyclical, “Laudato Si,” boldly addresses the ecological crisis as a moral issue that demands urgent attention. In this landmark document, the Pope emphasizes the interconnectedness of all creation and the obligation of humans to care for the environment as stewards of God’s gift.
The encyclical calls for a profound shift in attitudes, urging the faithful to recognize the environmental degradation caused by human activity. Pope Francis critiques consumerism and a “throwaway culture,” calling for a collective commitment to sustainable living. His message goes beyond theological discourse, extending an invitation to people of all faiths and those with no religious affiliation to join hands in safeguarding the planet.
The Catholic Church’s engagement with climate change is not limited to rhetoric. Pope Francis has made substantial strides toward greening Vatican City, installing solar panels and committing to carbon neutrality. These actions reflect a tangible commitment to the principles outlined in “Laudato Si” and serve as a model for other religious institutions.
The 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP28) offered various platforms and hosted several events for religious institutions and leaders to partake in.
The Faith Pavilion at COP28 was a key platform for religious engagement, providing opportunities for faith leaders to call for climate action and engage in discussions on the ethical responsibilities of faith leaders in addressing the climate crisis.
Additionally, the COP28 Presidency designed a series of interfaith initiatives, including the Confluence of Conscience, a global summit for faith leaders, to collectively address the findings of the Global Stocktake and sign a declaration to progress climate action at COP28.
The Interfaith Coordination Group on Climate Change served as a coordination hub for collaborative interfaith engagement towards COP28. Furthermore, the Talanoa Interfaith Gathering at COP28 will offer a platform for faith communities attending COP28 to share their initiatives, concerns, and hopes in their work for climate justice under a Talanoa dialogue framework. The Talanoa dialogue framework, originating from indigenous Fijian culture, is a method of problem-solving and decision-making that encourages participants to address three key questions: “Where are we? Where do we want to go? How do we get there?”. This gathering provided an opportunity for participants to engage in small-group Talanoa dialogues, an interfaith spiritual service, and a shared meal for those attending in person.
Despite these promising developments, several challenges remain in fully harnessing the potential of religious institutions to influence the outcome of COP28 and beyond. One key obstacle lies in the diverse perspectives within religious communities. While many faiths embrace environmental responsibility, others may hold different interpretations of scripture and theological views on the environment. This diversity may lead to internal disagreements and hinder unified action. Additionally, religious institutions themselves may face internal challenges in implementing sustainable practices within their own communities and overcoming resistance from traditionalist segments of their membership.
Furthermore, religious communities often lack the technical expertise and resources necessary to effectively engage in complex climate negotiations. Building capacity within faith-based organizations and fostering collaboration with scientific and advocacy groups is crucial for amplifying their voices at COP28 and ensuring their participation in policy discussions. Additionally, navigating the complex geopolitical landscape of international climate negotiations can be challenging for religious actors unfamiliar with the intricacies of international diplomacy.
Despite these obstacles, the presence and influence of religious communities at COP28 were undeniable. By building bridges between diverse faiths, investing in capacity building, and amplifying their voices, religious actors can play a pivotal role in shaping the global conversation on climate change and driving meaningful action. COP28 presented a unique opportunity for faith to transcend its traditional boundaries and become a powerful force for positive change in the fight against climate change.
Dr. Kristian Alexander is a Researcher at TRENDS Research & Advisory and an adviser at Gulf State Analytics, a Washington-based geopolitical risk consultancy. He has worked as an Assistant Professor at the College of Humanities and Social Sciences at Zayed University in Abu Dhabi, UAE. Dr. Alexander’s papers have been published by numerous outlets, such as the Middle East Institute, The Arab Gulf States Institute (AGSIW), International Policy Digest, International Institute for the Middle East, and Balkan Studies (IFIMES), Inside Arabia, and Fair Observer. His research examines social movements in the Middle East and security-related issues, with a particular interest in migration in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC).
This piece was originally published in Modern Diplomacy on December 14th, 2023.